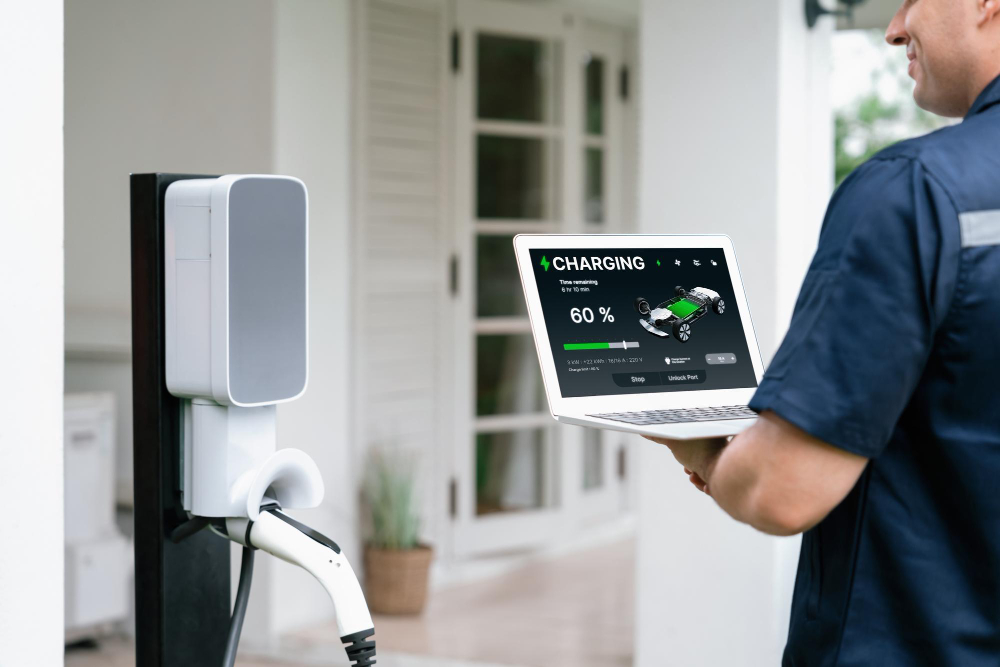
Electric vehicle adoption across Australia is accelerating, and with it comes a fundamental shift in how we fuel our cars. The real convenience of EV ownership comes from charging at home means you can start each day with a full battery without detours, queues or time wasted. However, installing a home charging station requires more than simply mounting equipment on your wall. Your electrical system, choice of charger, and installation approach all play crucial roles in creating a safe, efficient setup.
Will Your Home’s Electrical System Handle EV Charging?
Most Australian homes operate on single-phase power, which handles EV charging effectively but at moderate speeds. Three-phase power which is more common in newer properties, enables significantly faster charging provided your vehicle supports it. A licensed electrician can quickly determine which system you have and what it means for your charging capabilities.
Older homes present additional challenges as outdated switchboards and wiring weren’t designed for the continuous load an EV charger demands. If your home was built before 2000, still has a fuse box rather than circuit breakers, or you’ve never had electrical work done, an upgrade is highly likely. These are essential safeguards against overloading that could compromise your home’s electrical safety.
For households running multiple high energy appliances simultaneously, load management solutions become important. Modern load management technology intelligently distributes power to prevent issues while maintaining efficient charging.
Understanding Home EV Charging Requirements
The first step to preparing your home is knowing exactly what’s required. A home charging station isn’t just about plugging into an existing outlet. You’ll need an EV charger that works with your vehicle, charging cables long enough to comfortably reach your parking spot, and a reliable power supply that matches the charger’s demand. Ideally, the charger should be placed in a secure, dedicated space such as a garage or carport where it’s safe from weather extremes and easily accessible.
Before you rush into buying equipment, it’s a good idea to consult a licensed electrician. They’ll determine if your current wiring and switchboard can handle the extra load. If your home has older wiring or lower capacity, you may need an upgrade before installing the charger. Having the right infrastructure in place ensures charging remains smooth and safe, without putting unnecessary stress on your electrical system.
Electrical Capacity and Upgrades
Not all homes are automatically ready for EV charging. A key factor is whether your property has a single-phase or three-phase power supply. Single-phase is common in most homes and can charge an EV effectively, though at a slower rate. Three-phase power on the other hand, supports faster charging if your car is equipped to handle it.
Older properties might also have outdated switchboards or wiring that can’t support the demands of a modern charging station. If this is the case, an electrician will likely recommend a switchboard upgrade and installation of a dedicated circuit breaker. These steps are essential to prevent overloading, which could otherwise lead to safety risks. Load management solutions may also be introduced if you run several high-energy appliances alongside your EV charger. By preparing your home’s system properly, you’ll have peace of mind knowing that charging is safe, efficient, and future-proof.
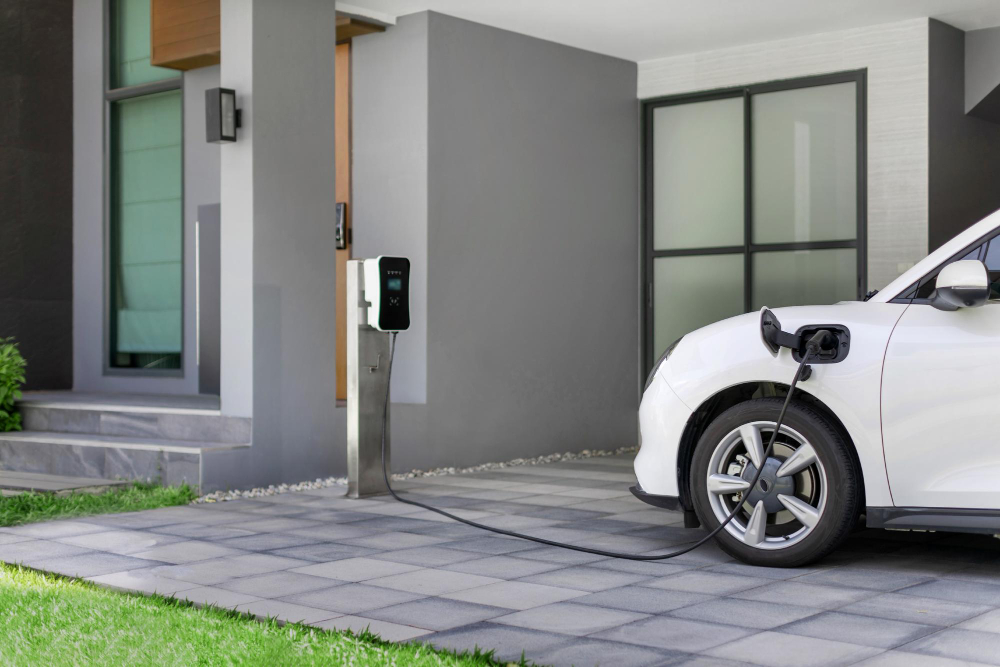

Choosing the Right Charger for Your Driving Habits
The type of charger you choose should reflect how often and how far you drive. Here is some details about the different types:
Level 1 chargers plug into standard household outlets and require no special installation. They’re the slowest option, typically adding around 100 kilometres of range over 8-10 hours. For drivers covering minimal distances daily, this basic solution might suffice. However, most EV owners quickly find Level 1 charging too limiting.
Level 2 chargers dominate the Australian residential market for good reason. They require professional installation and a dedicated electrical connection, but deliver substantially faster charging—often adding 30-50 kilometres of range per hour. If you drive more than 50 kilometres daily, take occasional longer trips, or simply value flexibility, Level 2 is the practical choice.
Level 3 chargers (DC fast chargers) remain impractical for homes due to their infrastructure demands and cost. These belong in commercial and public settings.
Beyond charging speed, consider smart charging features. WiFi-enabled chargers let you monitor energy consumption, schedule charging during off-peak electricity rates, and integrate with solar systems, capabilities that deliver ongoing savings.
Installation Location is More Important Than You Think
Where you install your charger directly impacts its longevity, safety, and daily usability. The location should align with your actual parking habits, with cable length accommodating your routine without creating trip hazards.
Even outdoor-rated chargers benefit from weather protection. Australia’s harsh sun degrades equipment faster than sheltered installations. Positioning your charger under eaves or in a carport extends its lifespan and reduces maintenance needs.
Making Your Home Charging Decision
The transition to home EV charging represents a significant investment, and success requires professional expertise from initial assessment through installation and beyond. Qualified EV installers ensure your electrical system handles the load safely, match equipment to your specific needs, and create compliant installations that deliver reliable service for years.
If you’re ready to get started then get in touch as we specialise in professional EV charger installation for Australian homes, businesses and public spaces. We conduct comprehensive property assessments, recommend optimal solutions and install your charging system to the highest safety standards.